In a world increasingly reliant on smart technologies, voice-controlled doors represent a significant advancement in the realm of accessible and secure entry systems. What was once the stuff of science fiction is now becoming an important tool in revolutionizing access control. With attention to ease, increased security, and accessibility, voice-operated doors are leading the way in innovation, affecting residential spaces as well as business and public spaces alike. In this article, the dramatic impact of voice-activated entry solutions is examined, examining their technical foundation, industry trends, challenges experienced, and prospects for the future.
Industry Context: Redefining Modern Entryways
The global market for smart entry systems and smart locks is projected to reach $11.88 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 19.4%.
The growth that we are experiencing is being fueled mainly by developments in smart home systems and the integration of voice recognition technologies with IoT devices like Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa. Voice-operated doors are an important part of this revolution, offering hands-free entry for homeowners, businesses, and institutions. Demand is also bolstered by government and organisational initiatives to improve accessibility standards, such as the European Accessibility Act and ADA standards in the U.S. These standards emphasize the need for inclusivity by mandating technologies that cater to the needs of older people and people with disabilities.
Recent Developments and Trends
Installation of voice-operated doors has dramatically grown in various industries. Major trends that drive the industry are:
- Integration with IoT and AI: Devices with AI-based voice recognition are being upgraded with deep learning abilities to distinguish between licensed users and potential intruders. For example intelligent locks that integrate with virtual assistants, can now recognize multiple voices and execute commands based on predefined user profiles.
- Hospitality and Commercial Applications:In the hospitality and commercial spaces, hotels are starting to incorporate voice-enabled locks to provide a more convenient guest experience. These devices seamlessly integrate with mobile apps, allowing for the electronic exchange of digital keys and obviating the need for physical keys or cards.
- Contactless Solutions: The COVID-19 pandemic has greatly increased the need for touchless systems. Voice activation reduces the risk of contamination, making it a popular choice in healthcare facilities and public offices.

Technology and Innovation Insights
At the center of voice-controlled doors is a high-level integration of advanced voice recognition capabilities and biometric security systems. Real-time verification, secure communication protocols, and remote monitoring are becoming more and more prevalent.
- Biometric Security: Modern systems embrace not just voice commands but also facial and fingerprint scanning, all in an attempt to ensure that security is provided at multiple levels.
- Cloud Connectivity: With the merging of IoT, users can connect remotely and be managed via smartphone, giving customers the ability to control their entry systems anywhere they go.
- Interoperability: Modern systems interconnect seamlessly with numerous smart home devices, such as cameras, doorbell units, and motion detectors, offering an integrated security solution.
A compelling example is the August Wi-Fi Smart Lock, which not only supports voice commands but also integrates with smart home ecosystems for a comprehensive experience.

Key Players and Stakeholders
Several industry leaders are at the forefront of this technological shift:
- Amazon (Alexa): Revolutionizing voice-controlled systems through enhanced AI capabilities, allowing smart locks and doors to integrate seamlessly into users’ daily lives.
- Google (Nest Ecosystem): Offering robust interoperability between voice-activated locks and other home automation devices.
- Assa Abloy: A pioneer in entry systems, with innovative solutions catering to commercial and residential markets.
- Local Startups: Companies such as Open Sesame have brought specialized solutions for wheelchair users, underscoring the accessibility aspect of the technology.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its potential, the adoption of voice-controlled doors faces challenges:
- Security Concerns:Unauthorised entry via voice forgery or hacking remains a formidable challenge. To address this problem, there needs to be active pursuit of advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication processes.
- Cost and Awareness: High initial costs and inadequate consumer education in emerging regions hinder widespread adoption.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adds another level of complexity to product development by guaranteeing systems are compatible with international accessibility standards.
Nonetheless, opportunities abound. As urbanization accelerates and smart cities proliferate, the demand for advanced security systems will skyrocket. The hospitality and healthcare industries, in particular, represent untapped market potential.
Data and Forecasts
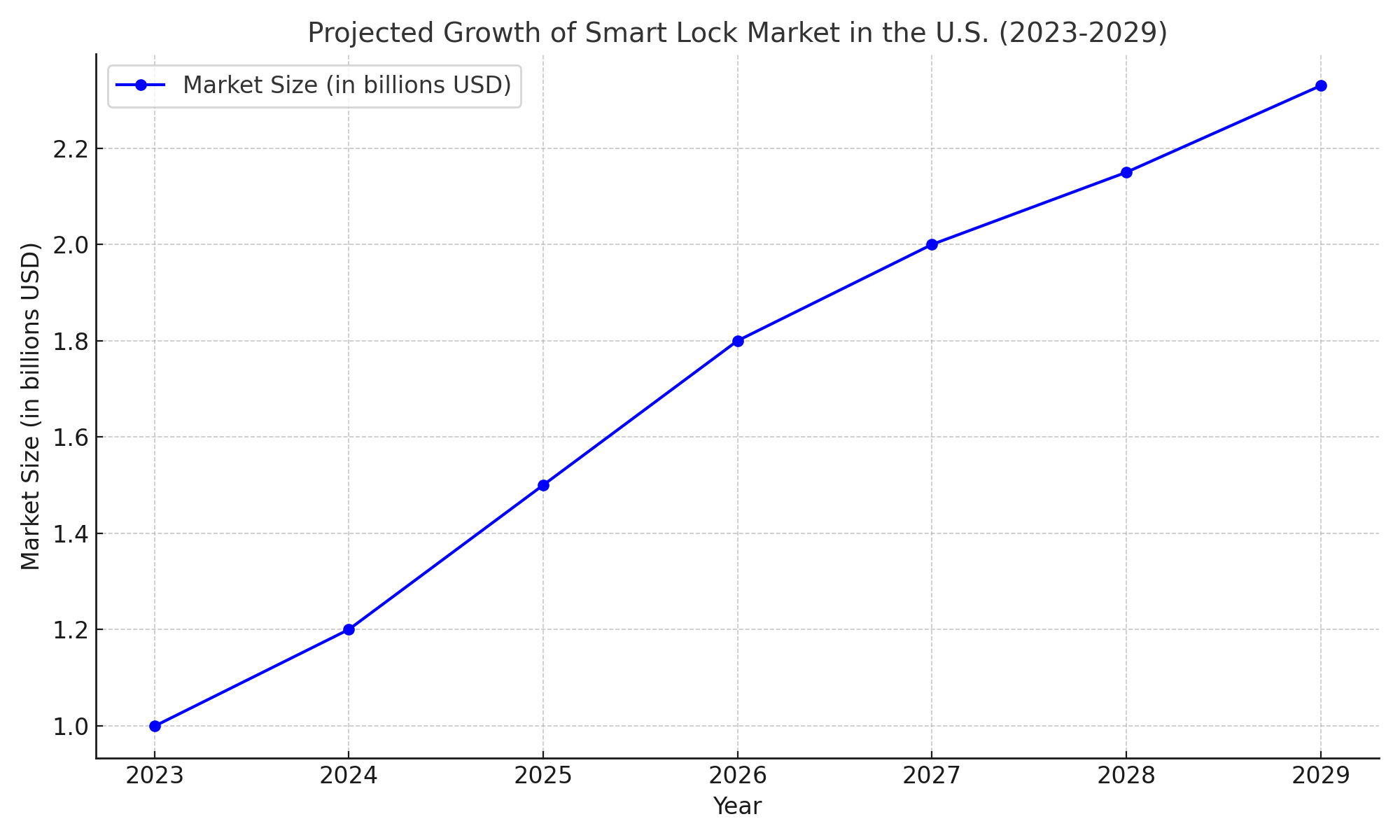
The expected increase in global voice-activated door system adoption is large. The US smart lock industry, which has a market value of $999 million in 2023, is expected to expand to $2.33 billion by the year 2029. The integration of voice control features, which is preferred by 45% of smart lock customers, is driving this growth.
Moreover, the rise of government-backed smart city initiatives, exemplified by India’s Smart Cities Mission, further underscores the expanding market for these innovative systems.
Future Outlook
The history of voice-assisted doors is about to be revolutionary. As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, these systems will provide predictive functionality, which will allow them to anticipate user behavior in order to maximize both security and convenience. The progress of self-learning algorithms combined with more robust encryption protocols will combat current security challenges effectively.
In the future, we can expect voice-controlled doors to move beyond their present applications in homes and companies to larger applications, such as secure access within autonomous public transport systems and disaster relief centers. The idea of cohesive cityscapes, where accessibility is not only safe but also inclusive, is progressively becoming a reality.
Conclusion
Voice-controlled doors are a remarkable combination of convenience, security, and accessibility. Through addressing the limitations of traditional locking systems and leveraging the potential of AI and IoT, they are setting new benchmarks in entry system technologies. As we move towards a future marked by intelligence and inclusivity, voice-controlled doors are likely to play a central role in shaping secure and accessible living spaces.